The popularity of cloud computing has increased over the last few years due to the explosive use of the internet. From competitive tech companies to start-ups, everyone wants to get into this space. According to the research, about 94% of enterprises are using at least one cloud service today.
As the enterprises shift their infrastructure on the cloud, the need for cloud load balancing solutions arise to handle traffic spikes. They can rapidly autoscale in response to the level of demand. They play a crucial role in balancing the system performance by evenly distributing the dynamic workload over multiple servers.
Leading cloud providers like Alibaba Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure, Google Cloud and IBM lead the cloud load balancer market. If you are wondering which solution you should opt for, here we list the major cloud load balancers and their features.

Source: Pixabay
Alibaba Cloud
Alibaba’s Cloud Server Load Balancer (SLB) redirects the incoming traffic among various instances to balance and improve the service capabilities of applications. It can process up to millions of requests all at the same time and quickly meet the requirements during large demands. This avoids service outrages.
It checks the service availability of ECS instances by performing health checks. In the case of unhealthy instances, it automatically removes them to avoid a single point of failure. You can also reduce the frequency of health check by increasing the interval time or changing a layer-7 health check to layer-4 health check based on the service condition.

Source: Alibaba Cloud
SLB also provides URL-based routing that allows users to redirect the incoming traffic to the backend server, based on URLs. This lets you configure the SLB across different zones of the region, so even if communication to one zone is interrupted, SLB automatically directs the traffic to zone 2 that is working normally.
Another important feature is Cross Region Disaster Tolerance through Global Traffic Manager (GTM), where we can configure SLB instances in different regions, and add ECS instances in various zones of the regions along with DNS service. The DNS service can resolve domain names, add IP addresses of different regions to different address pools of the Server Load Balancer and perform health checks. So, if a region becomes unavailable, this will automatically stop the domain name resolution for that unavailable region.
The price is calculated on the length of time of load balancer rentals and network traffic.
AWS
Amazon’s Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) can be used to distribute traffic across multiple EC2 instances. The service is elastic (i.e. changeable) and fully managed which means that it can automatically scale to meet demand.
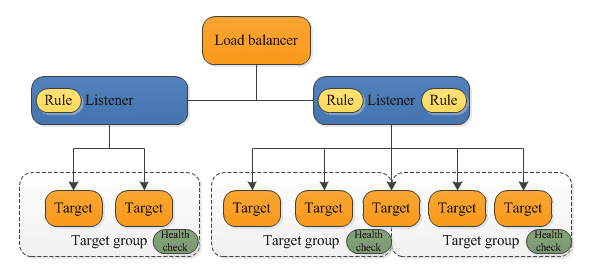
Source: AWS
There are three types of load balancers available in AWS.
Classic Load Balancer (CLB) operates on both the request and connection levels for Layer 4 (TCP/IP) and Layer 7 (HTTP) routing. It is best for EC2 Classic instances.
Application Load Balancer (ALB) works at the request level only. It is designed to support the workloads of modern applications such as containerized applications, HTTP/2 traffic, and web sockets.
Network Load Balancer (NLB) operates at the fourth layer of the (OSI) Open Systems Interconnection model. It is capable to handle millions of requests per second.
The pricing is based on the number of deployed load balancers and the data processed per hour.
AWS also provides third-party load balancing tools like Kemp LoadMaster and Barracuda Load Balancer in its Marketplace for more control. There is DNS based load balancing also which is offered through Route 53 which provides various routing and load balancing services. Route 53 is also useful in medical checks to send notifications through Cloud Watch.
Microsoft Azure
There are three types of load balancers in Azure: Azure Load Balancer, Internal Load Balancer (ILB), and Traffic Manager. The various load balancers ensure that the traffic is sent to healthy nodes.
Microsoft’s Azure Load Balancer offers a higher level scale with layer 4 load balancing across multiple VMs (virtual machines).

Source: Azure
Internal Load Balancer (ILB) has an internal-facing Virtual IP. Meaning, users can apply an internal load balancing for virtual machines (VM) that are connected only to an internal Azure cloud service or a virtual network.
Traffic Manager is an internet-facing solution that balances the traffic loads at various endpoints using a policy engine as well as a set of DNS queries. It can route traffic to any region’s service and even to non-Azure endpoints.
The pricing depends on the number of DNS queries received.
Azure also provides health check features that can be achieved through periodically polling an HTTP endpoint. It also provides third-party load balancing tools that are available in the Azure Marketplace.
Google Cloud
The Google Cloud Load Balancer (GCLB) provides server-side load balancing to distribute incoming traffic to multiple virtual machine instances. It allows users to direct applications across any region and scale compute with very little configuration. It can load 0-1 million requests per second with no pre-warming.

Source: Google
There are three deployment types of load balancing services in Google: Global, Network and Internal. Global Load Balancing supports HTTP(S) traffic for modern web-based applications. Traffic is distributed to the region that is closest to the calling user, provided the region has available capacity.
Network Load Balancing directs traffic across virtual machine (VM) instances in the same region in a VPC network. Any TCP and UDP traffic can be load balanced on the basis of source, destination port, and protocol so that the traffic from the same connection reaches the same server.
Internal Load Balancing is a regional load balancer that distributes the internal traffic across a set of back-end instances without requiring a public IP address.
The health check feature is set up within the Compute Engine of the UI. You can send health-related alerts and notifications on instance groups without the load balancer itself.
The pricing of GCLB is based on the amount of data processed.
IBM
The IBM Cloud Load Balancer (ICLB) distributes the load balance of traffic across multiple application server instances to improve uptime and scaling of application with minimum disruption.
In case of interruption to an entire zone, the applications work without any problem as the load balancer instances are divided across various zones of the same region. This enhances the security and availability of any application in the IBM Cloud.
It offers various load balancing options to choose from.

Source: IBM
IBM supports Multi-Zone Region (MZR) which means the load balancer nodes are instantiated in two different data centers. In case of an interruption to the data center communication, the load balancer will still continue to work, as the other node is a part of a different data center.
The load balancer allows medical checks periodically to check the health of the back-end ports and distribute the traffic accordingly. The health of the ports is continuously monitored until it successfully passes two consecutive health check attempts, Layer-4 for TCP ports and Layer-7 for HTTP port.
The pricing of ICLB is based on service usage hours, data processed and outbound public bandwidth depending on the geographic region.
If you have anything to add to the list, let us know in the comment section.
READ NEXT: Database Migration Comparison: AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, IBM, Alibaba Cloud









Nice article