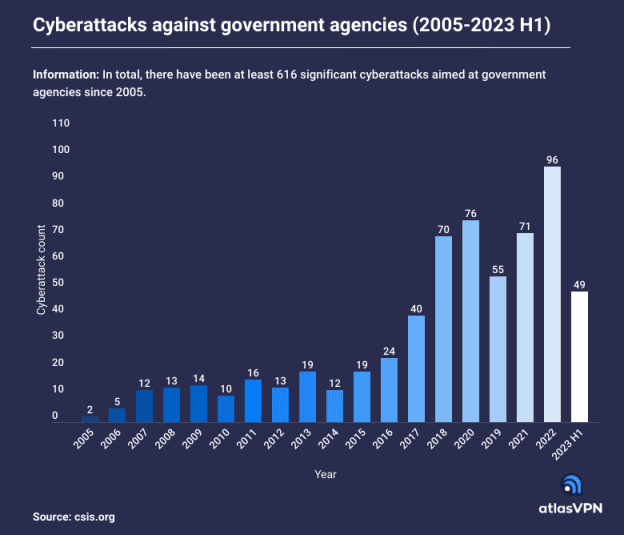
Based on the data provided by the Atlas VPN team, during the initial six months of 2023, there were 49 notable instances of cyber incidents involving governmental organizations. This marked an increase of 11% when compared to the corresponding period in the previous year. These attacks had an impact on governmental entities in a minimum of 27 countries globally.
The analysis is based on data provided by the Center for Strategic and International Studies, an organization dedicated to monitoring substantial cyber events. Our attention was exclusively directed towards incidents encompassing government establishments, their representatives, or contractors.
This year, government agencies within the United States faced the highest volume of attacks, with 16% of these being explicitly directed at the nation. Additionally, the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine has led to several cyber incidents targeting government establishments in both nations.
In case of potential perpetrators, Russian cyber attackers are prominently positioned, thought to be accountable for roughly 29% of these incidents. Following closely are hackers linked to China, contributing to 18% of the attacks, while Iran holds the third position with a 10% share.
Government entities accumulate and retain a substantial amount of confidential data, for example, personal information of citizens. This information can be traded on the dark web or seized until a ransom is paid. These factors make governmental agencies an attractive target for malicious cyber actors.
Beyond financial incentives, around 25% (12 instances) of global cyberattacks on government entities in 2023 can be attributed to state-linked threat actors immersed in cyberespionage campaigns. Furthermore, hacktivist activities played a significant role, contributing to roughly 10% of the documented cyber incidents within the governmental sphere throughout the initial six months of 2023.
Since 2005, governmental organizations on a global scale have encountered 616 noteworthy cyberattacks. A notable majority of these, equivalent to 56%, occurred within the last five-year span, including the initial half of 2023.








